SERVICES
A solar power plant is an arrangement of various solar components including solar panel to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, solar inverter to change the electricity from DC to AC as well as monitoring the system, solar battery and other solar accessories to set up a working system. It is an economic and a modern technique to generate electricity by solar panel using sunlight.
Grid-tied Solar Plant
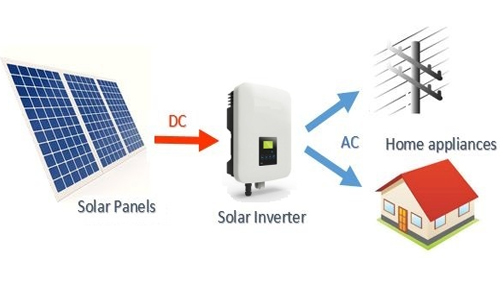
Typical Grid tied Solar Plant Diagram
Grid-tied solar systems - also known as on-grid solar - are the most popular kind of solar panel system. The beauty of a grid-tied solar system is that it creates a two-way relationship between your premises and the grid. In addition to importing power from the grid (as you already do), you can also export power to it. This means that during the day - when your solar panels are producing plenty of surplus power - you can actually export power to the grid. Your power exports earn you bill credits from the Power utility provider, dramatically reducing your power bill. The savings can be huge: possibly almost Zero.
Advantages:
- On-grid solar systems are very cost-effective and easy to install.
- Businesses can recoup the cost of their investment by offsetting electricity bills in just 3-8 years.
If a private, commercial or industrial building sets up a solar PV rooftop system it will be eligible to avail an ‘Accelerated Depreciation Benefit’ which is currently 80% in a year. At this rate, a business can completely depreciate the whole value of the project in approximately 4-5 years.
Zero Export Solar Plant
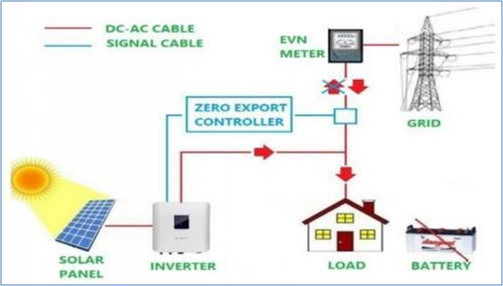
Typical Zero Export Solar Plant
To guarantee the Grid network’s stability, Utility provider may require limitations on injection into the grid network. This provision avoids excess injection, especially on weekends and public holidays in industrial buildings where the electricity demand is lower.
In some countries, the injection of electricity is prohibited: it is called zero export. In compliance with the law and to ensure the supply of a reliable electricity grid network to the end customer, some countries prohibit injection limitations. It avoids pollution of the network through the generation of “undesirable” harmonics. This interdiction helps to maintain a good quality network.
Take for example Morocco’s case; the opening of the electricity network to low voltage relative to self-generation relies on the principal supplier (ONEE) ability to find solutions to compensate for losses related to it. It presents a real shortfall for the latter and the twelve other distributors present in the country such as Lydec, Redal. Law 13-19 prohibits the self-producer from feeding back the energy produced to the grid, imposing conditions on PV systems, such as implementing a Zero Feed-in system when connected to the grid.
In concrete terms, Zero export implies:
- No part of the solar energy produced by the system is allowed to enter the grid.
- By default, excess solar energy is clipped by an injection limiter.
- A more economical approach, in which an intelligent energy management system is deployed, would optimize the amount of energy lost by clipping the right amount of solar-generated power.
Off Grid Solar Plant
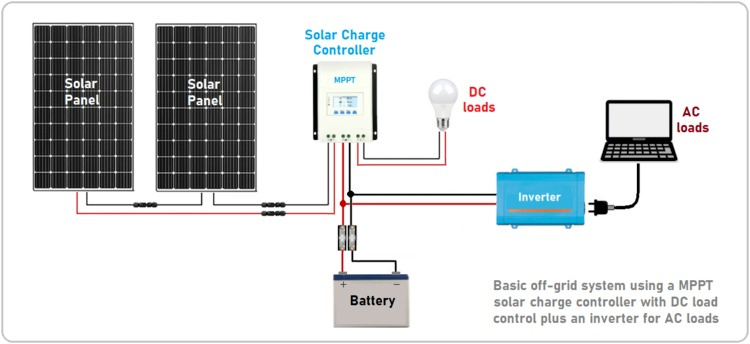
Typical Off Grid Solar Plant
Off-grid systems work independently of the grid but have batteries which can store the solar power generated by the system. The system usually consists of solar panels, battery, charge controller, grid box, inverter, mounting structure and balance of systems. The panels store enough sunlight during the day and use the excess power generated in the night.These systems are self-sustaining and can provide power for critical loads in areas where a power grid is not available. However, these systems require specialized equipment to function and can be costly to install. These are ideal for businesses which can sustain for a short period of time with no electricity.
Applications
- Electricity supply in rural and remote areas - Off-grid solar systems can facilitate independent, long-term and sustainable electricity generation in rural and remote areas.
- Power back up in areas with frequent electricity cuts - A number of places in India face frequent power cuts due to power transmission malfunctions, which can hamper operations of companies and public institutions. Off-grid solar systems can provide an economical and viable long-term backup solution to overcome the problems occurring during frequent power cuts.
Advantages
- These self-sustainable systems can work independently and do not rely on the grid.
- They generate enough power that can be stored and used at night or when the power grid is down.
- These are ideal for remote areas where there is no power access from the grid.
- Grid failures and shutdowns will not affect your power supply.
Hybrid Solar Plant diagram
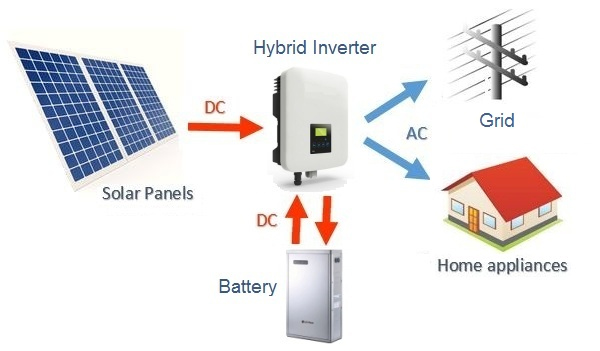
Typical Hybrid Solar Plant diagram
Hybrid solar systems generate power in the same way as a common grid-tie solar system but use special hybrid inverters and batteries to store energy for later use.
This ability to store energy enables most hybrid systems to also operate as a backup power supply during a blackout, similar to a UPS system.
Traditionally the term hybrid referred to two generation sources such as wind and solar, but in the solar world, the term 'hybrid' refers to a system which uses a combination of solar and batteries that can interact with the electricity grid.
Why you need O&M help?
O&M (Operation&Maintenance) is a programs we design for you which coordinate between best practices, tasks, and labor which will help your Solar PV systems to run efficientlyand properly in order to get the optimum energy production.
Our O&M system rest on three functions which are:
- Identification of the problem and solution
- Rectification of faults/errors to reduce downtime
- Detailed record keeping.
Our core competence in maintenance are based on:
- Preventive maintenance: Set periodical inspection and servicing of Solar PV equipment to make sure your Solar PV system will have minimum breakdown so that energy production losses could reduce.
- Corrective maintenance: Repairs/modifications after service/breakdown to minimize future downtime.
- Predictive or condition based maintenance: Predictive and condition based maintenance, both are forms of proactive maintenance aiming to anticipate and prevent solar PV equipment faults by using real-time data
Our main Monitoring system after commissioning/Installation of Solar PV system are:
- General data of Voltage, Current and performance
- Amount of Solar electricity generation in specific period
- Solar electricity consumption in specific time period
- Wear and tear condition of cables, connectors and switches
- Status of individual Solar PV system and its elements
- Solar PV DC to AC conversion efficiency
Cleaning

To remove a layer of dust, soils, bird droppings, Solar modules are washed with demineralized water. If the module has thick mud, dirt or bird droppings, which are sometimes requires extra efforts to remove, cold water is used, and the module surface is cleaned with a sponge.
A visual inspection of the solar module is done periodically to find defects such as broken solar cells, chips, de-lamination, fogged glazing, water leaks and discoloration. If any of the above defects are found, location is noted down in the system logbook and monitored for power generation output. If these defects causes the solar modules to perform lower than the rated value by the module manufacturer, replacement would be recommended.
Defect Checking:

Broken/Chipped solar cells
Broken and chipped solar cells are common and can indicate different issues. If several solar modules have chipped solar cells, your electricity production may reduce
Solar cell may has been damaged during handling or installations.
As you can see this defect can be easily spotted by performing a visual inspection. Also the problem is visible during an Electroluminescence (EL) test.
Our quality inspection person on-site can trace the exact cause and correct the defects by advising replacement

Scratches on solar module glass
With our experience, we have found major and prevalent quality issue are scratches on the glass cover of the solar module.
On average, small and large scratches on the thin glass covers are found during more than 70% of our quality inspections
These scratches are in many cases a result of improper handling during installation
Scratches, small and large, potentially lead to output degradation of the affected module. While less severe scratches superficially may cause some slight shading on the cells, larger and deeper scratches can heavily compromise the sensitive and nanometer-thin anti-reflection coating on the solar module, impacting the transmittanceof light.
The coating being damaged, air, dust, soil and water can get underneath which then causes the lifting of the rest of the coating and in the long run cause a delaminating effect.

External particles inside the solar module
Another defect you can easily spot yourself are external particles inside the solar module.
These particles may vary, including simple soldering debris (often small pieces of tab wire), cloth or even insects.
Debris the size as per below sample picture will have the same effect as shading and will, due to the cell-string structure of solar modules, affect its electricity production significantly.
Moreover, with the exposure of the solar module to sunlight, the particle may heat up, even burn, may cause severe damage to the module and moreover the whole system and project…

Solar cell string alignment
A misplaced string alignment is usually an aesthetic problem.
It usually won’t affect the solar module’s performance or lifetime.
However, String alignment is easily picked up by our quality personnel.
Also: if the spacing between the solar cells is too small (standard is 2mm), it may cause arching.

Fading labels and bar codes
As per The International Electro-technical Commission (IEC), every solar module needs to have a barcode encapsulated inside the PV module behind the glass.
This is important because in case of a warranty claim, customer need to present the barcode number to the manufacturer.
Most of the professional manufacturers around the world have databases where they can trace the date the module was bought, check the Bill of Materials and which distributor bought the module in specific country.
What if the barcode is not included inside the solar module?
In that case you better have a high quality barcode and label on the outside (back of the Solar module).
We perform the quality of these labels on the outside, by rubbing the label for a couple of seconds with some pure alcohol and a cloth. If the text/barcode comes off, the manufacturer has used a cheap label thus we replace these labels for future claim.
Module Structure Stability

Solar module mounting frames are inspected to make sure that the frames and modules are firmly secured, and mounting bolts are rust free. Junction boxes are inspected to ensure that the wires are not chewed by rodents or insects or by wear n tear
Inverter / charge controller:
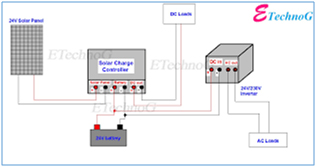
This component is maintained by minimizing dust accumulation. A dry cloth is used to wipe away any accumulated dirt/dust. After which a visual inspection ensures that all the indicators such as LED lights are working and the wires leading to and from this device are not loose. If self-checks are done, note that the charge controller should indicate that the system is charging when the sun is shining.
Wiring and connections:

Wiring installations are regularly checked for any cracks, breaks or deterioration in the insulation. Panel boxes are scrutinized to prevent the box becoming a home for rodents and insects. Moreover, the connections are inspected for corrosion and/or burning.
